CELLS
- Living things are made of cells
- There are many types of cell that make up a human body
- Cheek cells – Form
a hard wearing lining to your mouth
- Red blood cells – Carry
oxygen around your body
- White blood cells – Help
your body fight disease
- Sperm cells – Male
reproductive cell
- Ovum – Female
reproductive cello
- And many more
Parts of a Cell
The main parts of an animal cell are:
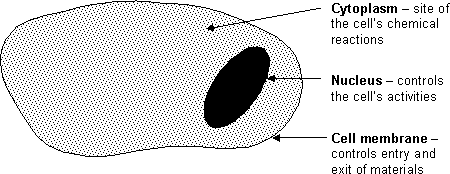
- The main parts of a plant cell are:
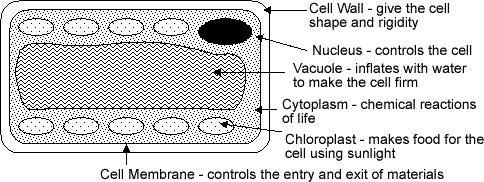
Photosynthesis
- In the chloroplast the plant makes food for itself by
photosynthesis

- Photosynthesis is:
- A chemical process
- that uses the energy in sunlight
- to turn the simple materials carbon dioxide and water
- into the complex material; sugar.
- Oxygen is a waste material from this process.
- The word equation for photosynthesis is:

- The sugar is stored in the cells as starch
- So we can tell if photosynthesis is occurring if we
test the leaves for starch

- cut out leaf discs using a cork borer
- boil the leaf discs in water for 2 minutes
- boil the leaf discs in alcohol until all the colour has gone
out of them
- place the leaf discs in a sample tray
- cover them with iodine
- if the disc turns black then starch is present
RESPIRATION
- The chemical reactions of the cell occur in the
cytoplasm
- One of the most important is respiration
- Respiration is:
- A chemical process
- That releases energy for the cell from sugar
- To do this the cell requires oxygen
- The waste materials from this are carbon dioxide and
water
- The word equation for respiration is:

- All the chemical reaction in the cell are carried out
by enzymes
ENZYMES
- Enzymes are:
- Complex chemicals
- That speed up chemical reactions
- Without being changed themselves
- An example of an enzyme is amylase
- Amylase is found in saliva
- Amylase turns starch in sugar

- There is a temperature at which the enzyme works best
- Above a certain temperature the enzyme is destroyed
and will no longer work
- pH

- There is a pH at which the enzyme works best
- This enzyme works best at an acid pH
- Other enzymes work best at other pHs
The Microscope

- using a microscope correctly
- carry it by the neck
- always have the smallest objective in place before you
place a specimen onto the stage
- always have the smallest lens in place when removing a
specimen
- only use the highest power with slides that have cover
slips
ADAPTATION OF CELLS

- Cells are well
adapted to their functions
- Sperm cells have a tail to swim
- Cheek cells form flat sheets
- Red blood cells are tiny and flexible to fit through
narrow tubes
REPRODUCTION
- To reproduce the male sex cell and the female sex cell
of any living thing must meet and join together.
- When the male sex cell and female sex cell meet and
join it is called fertilisation
- In plants the male sex cell is called the pollen and the female sex cell is
called the ovum (pl. ova).
In Plants


- The main parts of the reproductive system of a plant
are:

- Pollination is the
process where the pollen gets from the anther to the stigma.
- Some plants use the wind to blow the pollen from one
flower to another
- Some plants use insects like bees to carry the pollen from one flower to another
- Some plants use birds like the humming bird to carry pollen from one flower to another
- Once the pollen is on the stigma fertilisation can take
place
- The pollen tube grows out of the pollen and grows down
to the ovum
- The pollen nucleus travels down the tube and joins
with the ovum nucleus.
|
 |
In Animals
- In animals:
- the male sex cell is the sperm
- The female sex cell is the ovum
- The life cycle of an animal:

- Some animals use external fertilisation
- The female lays her eggs in water
- The male then fertilises them with his sperm
- The sperm swim through the water to the ovum
- Fish and amphibians use this method
|
 |
- Some animals use internal
fertilisation

- The male places his sperm inside the female
- The sperm swim through the female’s reproductive
system to find the egg
- Fertilisation occurs inside
the female
- Reptiles, birds and mammals use this method.
Puberty
- During puberty the human body becomes ready to reproduce
- Puberty occurs between the ages of about 11 and 16
- Hair grows on the body of both boys and girls
In females:
- Breasts and sexual organs develop
- Hips broaden
- Voice changes
In males:
- Sexual organs develop
- Shoulders broaden
- Strength increases
- Voice deepens
- In males organs of human reproduction are:

- In
females organs of human reproduction are (looking from the front):

- In mammals the process of fertilisation is:
- intercourse (passing sex cells to
the female)
- ejaculation (sperm are deposited in
the vagina at the end of intercourse)
- sperm swim along moist walls of the uterus and oviduct
- an egg is released from the ovary
- the egg travels down the oviduct
- the egg meets the sperm at the turn in the oviduct (marked
on the diagram)
- the sperm nucleus and egg nucleus fuse to form a fertilised
egg.
Development
- Once the egg is fertilised the development of the embryo begins:
- an embryo is a baby in its first eight weeks of
development

- The egg begins to divide an becomes an embryo
- The embryo joins to the wall of the uterus
- The embryo grows an umbilical cord and placenta
- The umbilical cord joins the embryo’s tummy button to
the placenta
- This allows food, oxygen and waste to pass between
the placenta and embryo
- The placenta connects the umbilical cord to the
uterus
- This is the site where food, oxygen and waste pass between
the mother’s blood and the embryo’s blood
- Eight weeks after fertilisation the baby is a recognisable
human being and it then called a foetus
- the foetus is surrounded by a protective, water
filled sack called the amnion
- the amnion and the fluid protect the foetus from
bumps and knocks.
- About 38 weeks after fertilisation the baby is born
|



















